cpp ] #cpp 单例模式的n种写法
Meyers 单例
C++11 标准规定: static local 的变量会保证初始化一次,并且是多线程安全的。由此我们可以得到这样的单例实现。
static local 的变量只有在第一次执行的时候才会初始化.
meyers_singleton.cpp 代码如下:
1 #include < iostream> 2 #include < thread> 3
4 class Singleton
5 {
6 public :
7 static Singleton & get_instance ( )
8 {
9 static Singleton instance;
10 return instance;
11 } 12
13 private :
14 Singleton ( ) = default ;
15 ~Singleton ( ) = default ;
16 Singleton ( const Singleton & ) = delete ;
17 Singleton ( Singleton && ) = delete ;
18 Singleton & operator= ( const Singleton & ) = delete ;
19 Singleton & operator= ( Singleton && ) = delete ;
20 } ;
21
22 int main ( void )
23 {
24 const int THREAD_NUMBER = 10 ;
25 for ( int i = 0 ; i < THREAD_NUMBER; i++ ) 26 {
27 std:: thread ( [ ] ( ) 28 { std:: cout << & Singleton:: get_instance ( ) << std:: endl; } ) 29 . join ( ) ;
30 }
31 std:: cout << & Singleton:: get_instance ( ) << std:: endl;
32 }
编译执行
1 g++ - std= c++11 meyers_singleton.cpp - o2 ./meyers_singleton 3 0x10dac20b0 4 ...省略... 5 0x10dac20b0
补充:C++ 中 static 对象的初始化
non-local static 对象(函数外)
C++ 规定,non-local static 对象的初始化发生在 main 函数执行之前,也即 main 函数之前的单线程启动阶段,所以不存在线程安全问题。但 C++ 没有规定多个 non-local static 对象的初始化顺序,尤其是来自多个编译单元的 non-local static 对象,他们的初始化顺序是随机的。
local static 对象(函数内)
对于 local static 对象,其初始化发生在控制流第一次执行到该对象的初始化语句时。多个线程的控制流可能同时到达其初始化语句。
在 C++11 之前,在多线程环境下 local static 对象的初始化并不是线程安全的。具体表现就是:如果一个线程正在执行 local static 对象的初始化语句但还没有完成初始化,此时若其它线程也执行到该语句,那么这个线程会认为自己是第一次执行该语句并进入该 local static 对象的构造函数中。这会造成这个 local static 对象的重复构造,进而产生内存泄露问题。所以,local static 对象在多线程环境下的重复构造问题是需要解决的。
而 C++11 则在语言规范中解决了这个问题。C++11 规定,在一个线程开始 local static 对象的初始化后到完成初始化前,其他线程执行到这个 local static 对象的初始化语句就会等待,直到该 local static 对象初始化完成。
Meyers 单例,带参数
static local 的变量只有在第一次执行的时候才会初始化.
meyers_singleton.cpp 代码如下:
#include < iostream> #include < thread>
class Singleton
{
public :
static Singleton & get_instance ( )
{
static Singleton instance ( param ) ;
return instance;
} static int param;
int storage;
private :
Singleton ( int m ) : storage ( m ) { } ;
~Singleton ( ) = default ;
Singleton ( const Singleton & ) = delete ;
Singleton ( Singleton && ) = delete ;
Singleton & operator= ( const Singleton & ) = delete ;
Singleton & operator= ( Singleton && ) = delete ;
} ;
int Singleton:: param = 0 ;
int main ( void )
{
const int THREAD_NUMBER = 10 ;
Singleton:: param = 222 ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < THREAD_NUMBER; i++ ) {
std:: thread ( [ ] ( ) { std:: cout << & Singleton:: get_instance ( ) << " value:" << Singleton:: get_instance ( ) . storage << std:: endl; } ) . join ( ) ;
}
std:: cout << & Singleton:: get_instance ( ) << " value:" << Singleton:: get_instance ( ) . storage << std:: endl;
} 编译执行
g++ - std= c++11 meyers_singleton_param.cpp - o./meyers_singleton_param ✔
0x108d32138 value:222
...省略... 0x108d32138 value:222
双重检测
#include < iostream> #include < thread> #include < atomic> #include < mutex>
class Singleton
{
public :
static Singleton & get_instance ( )
{
Singleton * ins = _instance. load ( std:: memory_order_acquire ) ;
if ( ! ins) {
std:: lock_guard< std:: mutex> lk ( _m ) ;
ins = _instance. load ( std:: memory_order_acquire ) ;
if ( ! ins) {
ins = new Singleton ( ) ;
_instance. store ( ins, std:: memory_order_release ) ;
}
}
return * ins;
}
private :
Singleton ( ) = default ;
~Singleton ( ) = default ;
Singleton ( const Singleton & ) = delete ;
Singleton ( Singleton && ) = delete ;
Singleton & operator= ( const Singleton & ) = delete ;
Singleton & operator= ( Singleton && ) = delete ;
static std:: atomic< Singleton * > _instance;
static std:: mutex _m;
} ;
std:: atomic< Singleton * > Singleton:: _instance;
std:: mutex Singleton:: _m;
int main ( void )
{
const int THREAD_NUMBER = 10 ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < THREAD_NUMBER; i++ ) {
std:: thread ( [ ] ( ) { std:: cout << & Singleton:: get_instance ( ) << std:: endl; } ) . join ( ) ;
}
std:: cout << & Singleton:: get_instance ( ) << std:: endl;
} 编译执行:
g++ - std= c++11 double_check_singleton.cpp - o./double_check_singleton
0x7fd638204080 ...省略... 0x7fd638204080 补充:
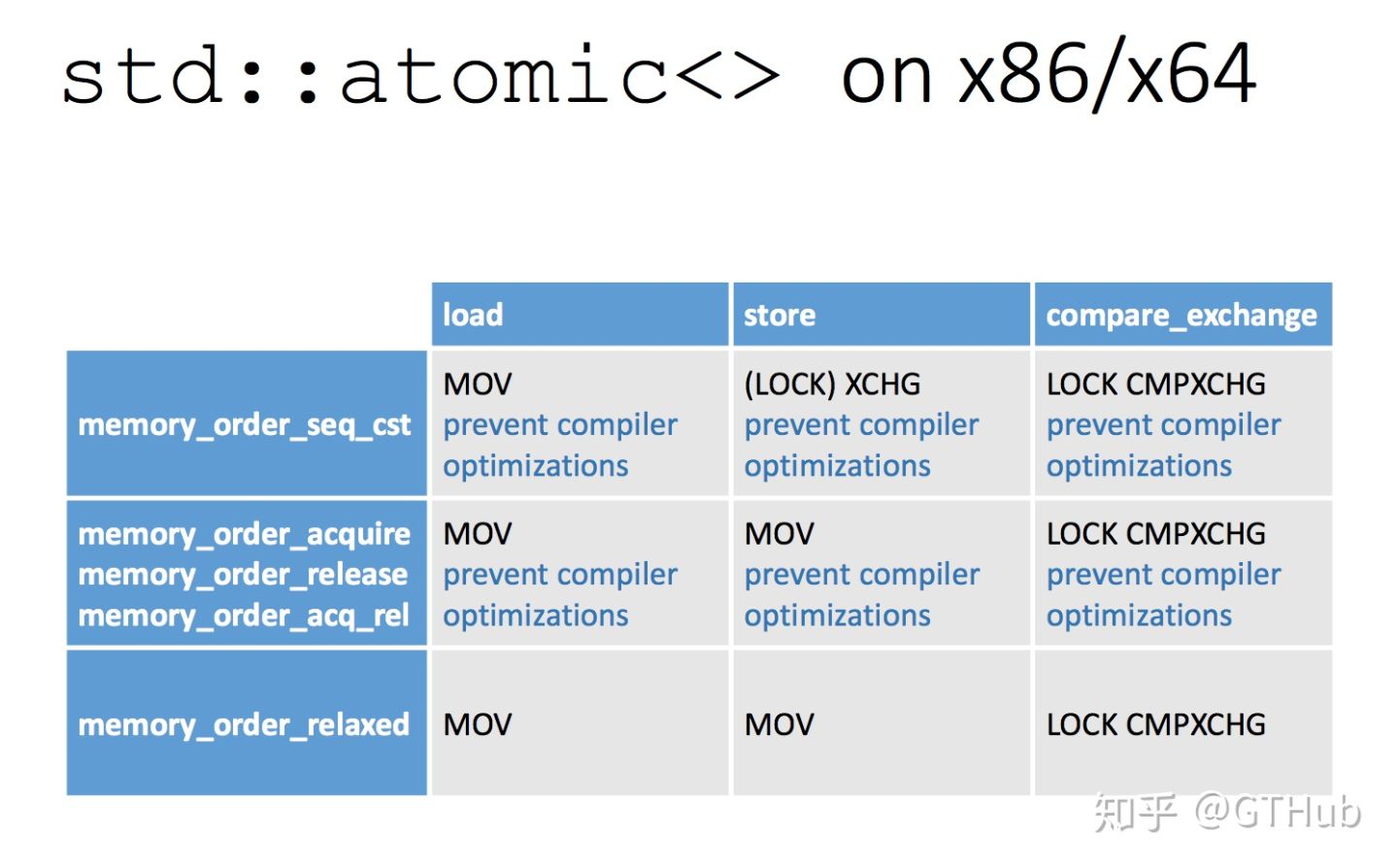
内存序参数 说明
memory_order_relaxed 宽松操作:没有同步或顺序制约,仅对此操作要求原子性 memory_order_consume 有此内存顺序的加载操作,在其影响的内存位置进行消费操作:当前线程中依赖于当前加载的该值的读或写不能被重排到此加载前。其他释放同一原子变量的线程的对数据依赖变量的写入,为当前线程所可见。在大多数平台上,这只影响到编译器优化 memory_order_acquire 有此内存顺序的加载操作,在其影响的内存位置进行获得操作:当前线程中读或写不能被重排到此加载前。其他释放同一原子变量的线程的所有写入,能为当前线程所见 memory_order_release 有此内存顺序的存储操作进行释放操作:当前线程中的读或写不能被重排到此存储后。当前线程的所有写入,可见于获得该同一原子变量的其他线程(见下方释放获得顺序),并且对该原子变量的带依赖写入变得对于其他消费同一原子对象的线程可见 memory_order_acq_rel 带此内存顺序的读修改写操作既是获得操作又是释放操作。当前线程的读或写内存不能被重排到此存储前或后。所有释放同一原子变量的线程的写入可见于修改之前,而且修改可见于其他获得同一原子变量的线程 memory_order_seq_cst 有此内存顺序的加载操作进行获得操作,存储操作进行释放操作,而读修改写操作进行获得操作和释放操作,再加上存在一个单独全序,其中所有线程以同一顺序观测到所有修改
c++ memory_order
call_once
保证 create_instance 被线程安全地调用一次
#include < iostream> #include < thread> #include < mutex>
class Singleton
{
public :
static Singleton & get_instance ( )
{
std:: call_once ( _flag, create_instance ) ;
return * _instance;
}
private :
Singleton ( ) = default ;
~Singleton ( ) = default ;
Singleton ( const Singleton & ) = delete ;
Singleton ( Singleton && ) = delete ;
Singleton & operator= ( const Singleton & ) = delete ;
Singleton & operator= ( Singleton && ) = delete ;
static void create_instance ( )
{
_instance = new Singleton ( ) ;
} static Singleton * _instance;
static std:: once_flag _flag;
} ;
Singleton * Singleton:: _instance = nullptr ;
std:: once_flag Singleton:: _flag;
int main ( void )
{
const int THREAD_NUMBER = 10 ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < THREAD_NUMBER; i++ ) {
std:: thread ( [ ] ( ) { std:: cout << & Singleton:: get_instance ( ) << std:: endl; } ) . join ( ) ;
}
std:: cout << & Singleton:: get_instance ( ) << std:: endl;
} 编译执行:
g++ - std= c++11 callonce_singleton.cpp - o ./callonce_singleton
0x7fef7d705bf0 ...省略... 0x7fef7d705bf0 单次检测法
每一次都要加锁和解锁
#include < iostream> #include < thread> #include < mutex>
class Singleton
{
public :
static Singleton & get_instance ( )
{
std:: lock_guard< std:: mutex> lk ( _m ) ;
if ( ! _instance) {
_instance = new Singleton ( ) ;
}
return * _instance;
}
private :
Singleton ( ) = default ;
~Singleton ( ) = default ;
Singleton ( const Singleton & ) = delete ;
Singleton ( Singleton && ) = delete ;
Singleton & operator= ( const Singleton & ) = delete ;
Singleton & operator= ( Singleton && ) = delete ;
static Singleton * _instance;
static std:: mutex _m;
} ;
Singleton * Singleton:: _instance;
std:: mutex Singleton:: _m;
int main ( void )
{
const int THREAD_NUMBER = 10 ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < THREAD_NUMBER; i++ ) {
std:: thread ( [ ] ( ) { std:: cout << & Singleton:: get_instance ( ) << std:: endl; } ) . join ( ) ;
}
std:: cout << & Singleton:: get_instance ( ) << std:: endl;
} 编译执行:
g++ - std= c++11 check_singleton.cpp - o./check_singleton ✔
0x7fc680705bf0 ...省略... 0x7fc680705bf0 饿汉模式
#include < iostream> #include < thread> class Singleton
{
public :
static Singleton * get_instance ( )
{
return singleton_;
}
static void destrey_instance ( )
{
if ( singleton_ != NULL ) {
delete singleton_;
}
}
private :
Singleton ( ) = default ;
~Singleton ( ) = default ;
Singleton ( const Singleton & ) = delete ;
Singleton ( Singleton && ) = delete ;
Singleton & operator= ( const Singleton & ) = delete ;
Singleton & operator= ( Singleton && ) = delete ;
private :
static Singleton * singleton_;
} ;
Singleton * Singleton:: singleton_ = new Singleton;
int main ( void )
{
const int THREAD_NUMBER = 10 ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < THREAD_NUMBER; i++ ) {
std:: thread ( [ ] ( ) { std:: cout << Singleton:: get_instance ( ) << std:: endl; } ) . join ( ) ;
}
std:: cout << Singleton:: get_instance ( ) << std:: endl;
Singleton:: destrey_instance ( ) ;
return 0 ;
} 编译执行:
g++ - std= c++11 ehan_singleton.cpp - o./ehan_singleton
0x7fa7f4f05ba0 ...省略... 0x7fa7f4f05ba0 参考资料
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/342769966
c++ memory_order
https://blog.csdn.net/u011726005/article/details/82356538
https://blog.csdn.net/lgfun/article/details/105810039